Types of business operation
When trying to establish a business in Japan, these are the three modes of business owners can choose from
①Representative office: this is usually a liaison office and doesn’t hold its own corporate legal status. Their main purpose is to conduct market surveys, or take care of the transactions between the business owner’s country and Japan, before the official incorporation of the company. These offices are not allowed to engage in sales activities or sign certain contracts in their own name. In case the company is sending over foreign employees to work at its representative office in Japan, they must have a valid residential address different from that of the office in order to qualify for the status of residence (as intracompany transferee).
②Subsidiary companies: As defined in Japan’s Companies Act , this refers to the action of investing a certain capital with the intention of opening up a company. The procedures needed are similar for foreigners and Japanese nationals. Once the establishments procedures for a company has been completed, they are allowed to engage in import and export of products and sales activities, as well as signing off contracts in their own name, and any other administrative procedures.
- Joint-stock Corporation (Kabushiki Kaisha): most common type of company
- Limited Liability Company (LLC, Godo Kaisha): This type of business structure has been adopted after the revision of Japan’s Companies Act in 2006. In the case of a joint-stock corporation, the size of the investment (duties) determines the dividend (rights) for the investors, but in an LLC, it is possible to stipulate specific investments options and share distributions percentages. It is important however to mention that, in Japan, LLCs are being called so simply because of the freedom of action, and that in reality, they do not offer the same advantages as LLC in foreign countries, such as benefits on the taxation system. Greater freedom of actions can encourage greater rivalry between investors, hence the importance of precise and detailed Articles of Incorporation.
- Other types of companies:other than NPOs, General Incorporated Foundations are also considered as nonprofit organizations. Educational institutions as well as social welfare institutions are also categorized as companies. Foreign investments into these type of institutions are however very rare.
These companies are commonly referred to as Domestic Corporations, as opposed to foreign corporations.
③Establishing a branch office in Japan: This is the procedure for opening up a branch office of a company in Japan. A preliminary requirement is to have an already established mother company operating according to the laws and regulations of the country of origin, and the range of activities within Japan will be the same as in the home country. In addition, the accounting books must be kept following the home country yearly schedule, which makes the procedures more complicated and in reality, the branching option is seldom chosen. Branch offices do hold their own legal corporate status and can be contract holders.
<Comparison of Representative office, subsidiary company and branch office>
| Representative office | Joint-stock Corporation (Kabushiki Kaisha) | Limited Liability Company (Godo Kaisha) | Branch Office | |
| Purpose of establishment | Market Surveys and success prospect, seeking business partners. Advertisement and promotion before establishment. Doesn’t hold its own legal corporate status. | Full-scale business activities in Japan. Multiple investors possible. Dividend ratio proportional to investment share. | Full-scale business activities. Multiple investors possible. Types of investments and dividend ratio can be defined in the Articles of Corporation. | Continuous business activities in Japan. Bank accounts settings, contracts, import/export and similar procedures can be completed under the branch’s name. |
| Main Actors | Company of home country | Corporation Representative | Corporation Representative | Legal representative in Japan |
| Responsibilities of Management | Since a representative office cannot sign contracts, company of home country is held responsible. | The joint-stock company director | The Limited liability company employees and the representative employee | Company of home country must be responsible for management. |
| Authentication of Articles of Incorporation by a notary public | Unnecessary | Necessary (authorization fee:\52,000;
Revenue stamp on the Articles of Incorporation:\40,000 |
Unnecessary (Note that an Articles of Incorporation document is still required) | Unnecessary
However, to prove existence of parent company, verification by a notary public in the home country is required |
| Public certifications required upon beginning of operations and establishment | None in particular | Founder and director’s seal (signature) impression certificate | Representative partner’s seal (signature) impression certificate | Certifications for the parent company in home country or Japanese certification |
| Registration Procedures | Unnecessary | Necessary | Necessary | Necessary |
| Capital transfer | Unnecessary | Remittance procedures can take a while, and in some cases are complicated. | Remittance procedures can take a while, and in some cases are complicated. | Unnecessary |
| Minimum registration license tax required ※ | None | \150,000. If capital exceeds \21,430,000, tax will be 0.7% of total capital amount. | \60,000 | Tax on nomination of a representative in Japan: \60,000
Tax on establishment of a business office in japan: \90,000 |
| Status of Residence to obtain for the predicted activities | Intra-company Transferee | Business Manager、Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/ International Services
|
Business Manager、Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/ International Services
|
Intra-company Transferee、Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services |
| Possibility of engaging in litigations | Not allowed. | The parent company is not allowed to.
Only allowed for the subsidiary in japan itself |
The parent company is not allowed.
Only allowed for the subsidiary in japan itself |
The parent company is allowed to. |
| Procedures for closing the business | None | Usual Procedures for dissolving/ liquidating a company.
Board General meeting of the shareholders |
Usual procedures for dissolving/liquidating a company.
General meeting of partners. |
Procedures for office closure. Can be a rather complicated process.
Can take time, including notice of closure. |
※Separate fees are applicable for seal stamps, rubber stamps, certified copy of register (certificate of registered matters) and if have the necessary documents prepared by a specialist.
Procedures for Establishing a Joint-Stock Corporation (Kabushiki Kaisha)
To establish a joint-stock corporation, it is necessary to list a number of important matters in the Articles of Incorporation, to have it notarized by a notary public and then registered at the Legal Affairs Bureau.
Below are the important items that must be included in the company’s articles of incorporation.
| Type of Information | Statement example/Special mention |
| Corporation Name | Ex: Sincere Trading Corporation
Verify through the Legal Affairs bureau/Internet, that the same or similar sounding corporation name doesn’t already exist. |
| Purpose | The statement should be detailed and clear on the purpose of business activities
Ex: For the purpose of manufacturing and selling ○○ machines → OK For the purpose of running a business → NG Furthermore, for management of businesses such as fishery, manufacture of leather products, manufacture related to weaponry, communication business, manufacture of biological products (vaccines), it might be necessary to notify the Bank of Japan in advance. |
| Head office location | Ex: Kanagawa Prefecture, Kawasaki City, Asaoku Ward xxxx
It is necessary to choose and secure a location beforehand. In principle, the manager (owner’s) house can be registered as an office, but it is necessary to confirm with the real estate contract that the rented place can be used for business purpose. Meantime, under a Business manager residence status, practice of business at one’s home is generally prohibited; hence it becomes necessary to secure an office anyway. |
| Structure establishment | Possibility to establish a company even with just one director. However, expansions in the future will require restructuration. |
| Authorized Shares | Ex: 1,000 shares
If a company plans of expanding its activities and issue a considerable number of shares in the future, it is preferable to set a large number of authorized shares in the articles of corporation, so that when the need to issue new shares present itself, shareholder’s general meeting and notification of changes can be skipped. |
| Shareholders general meeting resolution | Investors can decide by rule of majority to either tighten or lighten the requirements for a resolution, within the legal boundaries. |
| Number of directors | 1 or more |
| Fiscal year | Ex: April 1st to March 31st
Accounting period can be set at convenience. However most companies in Japan close their fiscal year in Japan in March, so by choosing a less busy time of the year, requesting a tax accountant will be easier. |
| Amount of capital | Ex:\10,000,000
Legally, Joint-stock Corporations can be set up with a capital amount as little as \1, but for non –Japanese nationals to obtain a visa under the “Business Manager” status, investment scale is actually required to be a minimum of \5,000,000. Remittance of capital from overseas can take time in some cases. |
| Number of shares issued at the time of establishment | Can be decided arbitrarily, as long as it is within the number of authorized shares. |
| Representative Director at the time of establishment | Ex: James Sincere
Nationality or place of residence does not matter. Up until now, it was required that at least one of the directors has a residential address in Japan. As of march 2015, a notification from the Ministry of Justice has revealed that registration applications can now be received even if none of the directors lives in Japan. However, without an address in Japan, it is difficult to open personal bank accounts, which makes the procedures complicated and cooperation from a Japanese partner might be necessary. |
| Founder | Ex: James Sincere
The founder is the individual who decided they wanted to operate a business and create a company. It can be one person or more. |
※This lists only the most important matters of the Articles of Corporation.
1) General flow of procedures for establishing a joint-stock corporation (Kabushiki Kaisha)
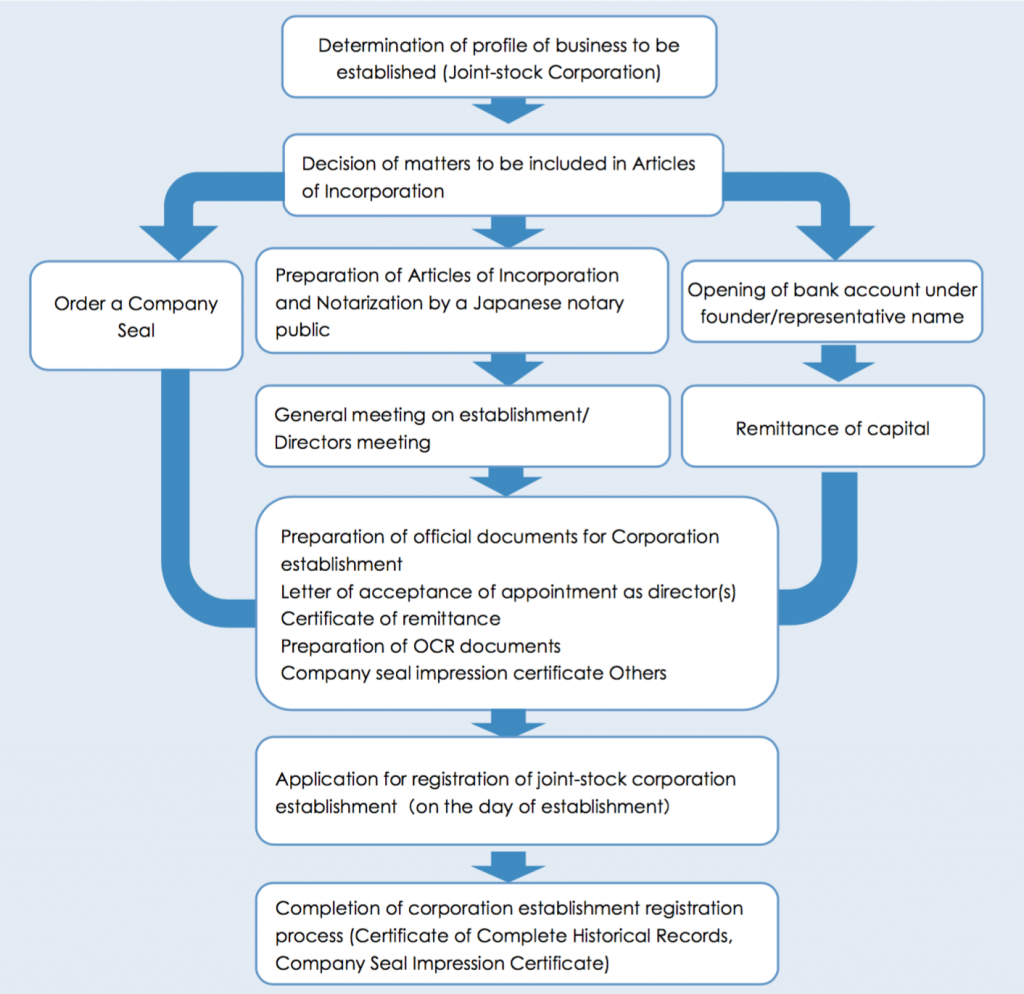
2) Obtaining licenses and permits
While there are activities that can be started at the owner’s convenience, for a number of them, it is necessary to obtain a license to engage in them or at least notify the adequate authorities.
The first step should be to figure out what licenses and notices are necessary. If a permit is needed, it is most likely that there will be specific requirements to meet regarding total of capital, net assets, qualified full time employee, the size and layout of the office, etc. As a result, it is essential to investigate and take note of all these details and establish your business in accordance of all the requirements.
<Required licenses/permit and governmental agency>
| Types of businesses | Governmental Agency |
| Food Manufacturing business, Food processing Business, Dairy sale business, Meat sale business, marine produces sale business, restaurants, cafes, beauty business, barber shops, cleaning business, hotel business, Public bath services, Entertainment industry, Medical care industry (corporate), Pharmacy, Pharmaceutical drugs sale, poisonous and narcotic substances sale, surgery industry (such as massages, acupressure therapy known as shiatsu), dental laboratory, Sales and rental of Medical Controlled Devices, Laundromat business, Coin-operated shower services. | Public Health Department |
| Recycling shops, secondhand bookstore, antique (second hand) store, pawnshop, Security Services, bars and pubs, Pachinko and other gaming stores (mah-jongg), replacement driver services. | Police Station |
| Liquor industry | Tax office |
| Industrial waste business, Domestic waste business, Electric construction business, business that handle explosives, Long-term Care Insurance business, Manufacture and sales of medicinal drugs, Manufacture and sales of cosmetic products, Manufacture and sales of medical equipment, Manufactures and Import of poisonous and narcotic substances, Elder care facility business,
Travel agency ( all four types) business, tour guide interpretation business, veterinary business, Real Estate business, Construction Business, Advanced vocational schools, other types of schools, Non-profit Organizations |
Prefectural and city offices
(Dep. Of Environment, Dep. Of Public welfare and Public health, Dep. of Industrial Labor, Dep. of Urban Development, Life, Culture and Sports Department, etc.) |
| Fee-charging/free employment agency, General/specialized worker dispatch business | Prefecture/city offices (Labor Department) |
| Freight transportation business, Passenger transport business, Car repair industry, Travel agency (international and domestic travels) | Prefecture/city offices (Transport bureau) |
3) Notifications required after registration
Once the incorporation process is complete, it is necessary to fill the following notifications and submit them to the authorities in charge.
| 1.National Tax office |
| (1)Notification of Incorporation (file within 2 months from date of corporation) |
| (2) Application for Approval of filing a blue form tax returns |
| (3)Notification of establishment of an office paying salaries(file within one month from office opening) |
| (4) Application for payment of withholding income tax on a semiannual basis |
| ※ With this application, the payment can be made every 6 months instead of monthly |
| 2.Prefectural Tax office |
| (1) Notification of Incorporation |
| 3.Municipal Tax office |
| (1) Notification of Incorporation |
| 4.Labor standards inspection office |
| (1) Notification of establishment of labor insurance relationship |
| (2) Declaration of estimated insurance distribution |
| ※Required in order to join the Worker’s compensation insurance system. |
| 5.Public employment security office(job-placement office) |
| (1) Notification of coverage of establishment by employment insurance |
| (2) Notification of acquisition of insured status |
| Covers worker’s insurance during unemployment, child care or family-care leaves |
| 6.Social insurance office |
| (1) Notification of first-time coverage by insurance |
| (2) Notification of first report of current state of affairs |
| (3) Notification of acquisition of insured status |
| ※Required in order to join health insurance, nursing care insurance and employee’s pension insurance. |
| 6.Bank of Japan |
| If non-Japanese nationals make up for more than 10% of the investors, it is required to notify the Bank of Japan before or after registration. |

 日本語
日本語 中文
中文